Diversification under Yield Randomness in Inventory Models
I haven’t really touched on the early research on risks in supply chain management. One major stream is on random yields. Parlar and Wang (1993) were one of the firsts to extend the classic Newsboy and EOQ (Economic Order Quantity) models to include uncertainty.
Models
Both models calculate the optimal inventory while including different cost factors (like setup cost for ordering, inventory holding cost) and decision variables (order volume and order timing).
As an extension the Newsboy problem also includes random demand.
Parlar and Wang now extended these models by a second raw material source and making the availability random of both sources. In this case the yield of the supplier is represented by a exponential distribution with two independent expected yield and standard deviation for both suppliers.
Results
An example of some numerical calculations done on the EOQ model is represented in figure 1.
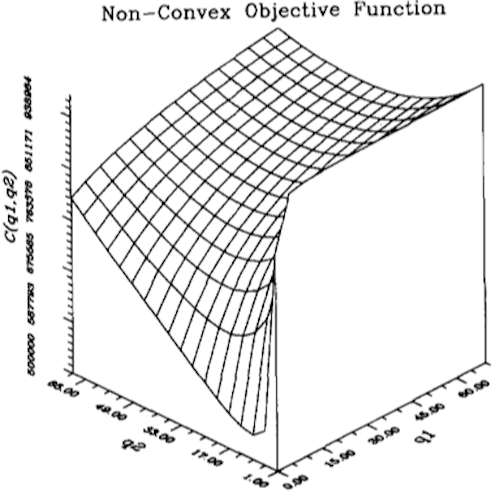
For both problems the authors find ways to calculate the optimal order decisions (figure 2, for the EOQ model). But they also admit that solving the newsboy problem required some extra effort and any addition to the model (like a third supplier) would make it even harder to solve.
Conclusion
These are operational models and they can and should be applied for operational decisions in inventory management and purchasing. But on the other hand they are also very abstract leaving many parameters out and (according to the authors) being hard to extend.
Parlar, M., & Wang, D. (1993). Diversification under yield randomness in inventory models European Journal of Operational Research, 66 (1), 52-64 DOI: 10.1016/0377-2217(93)90205-2



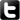




Add new comment