Improving Confidence to mitigate Supply Chain Risks
Yet another paper on risk mitigation strategies. This time: How to reduce risks by improving confidence. You can find the complete paper of today in the web.
Lack of Confidence
The authors theorize that especially demand risk (volatility) has increased during the last years. With several SC concepts which are aimed to reduce the slack in the supply chain during the same period, overall risks in the SC have increased dramatically.
This leads to a lack of confidence by the managers responsible for the SC in:
- Order cycle time
- Current order status
- Demand forecasts given
- Supplier’s capability to deliver
- Manufacturing capabilities
- Quality of the products
- Transportation reliability
- Services delivered
If you are still unsure if in your supply chain the lack of confidence prevails, have a look at this list.
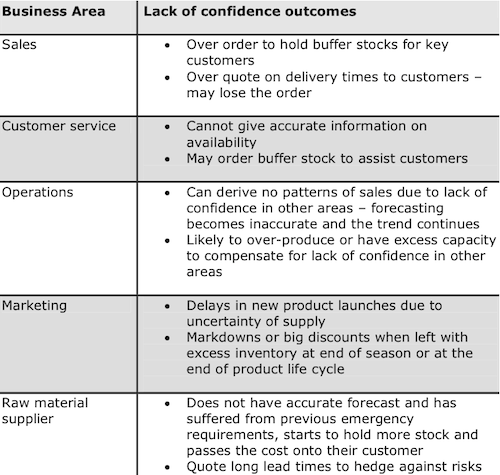
Risk Spiral
The lack of confidence can help to increase risks even further. Since according to the risk spiral, lack of confidence may lead to a increase of buffers in the supply chain to make sure that the product can still be delivered.
This on the other hand leads to longer cycle times / pipelines, which reduces the visibility even further.
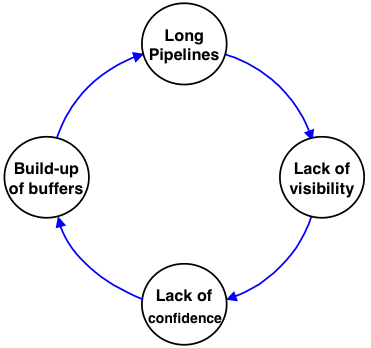
Solution
Instead of increasing buffers the authors recommend to improve visibility and control:
- Visibility
The key to improved supply chain visibility is shared information among supply chain members. Traditionally companies have tended to subscribe to the view that ‘information is power’ and to interpret the phrase as meaning power is diminished if that information is shared. In fact in supply chains the reverse is true. If information between supply chain members is shared, its power increases significantly. This is because shared information reduces uncertainty and thus reduces the need for safety stock.
- Control
The goal here is to improve flexibility over the supply and own processes. The time to react to the new information gained above has to be used well.
Conclusion
Visibility and control summarizes several existing strategies (like information exchange and reducing lead times) into a new concept for thinking about supply chain risk mitigation. It therefore has the potential to lead to new / better strategies to reduce risks. The table above can be used to analyzed if some supply chain is already affected by low confidence. From a scientific standpoint I am missing the grounds for this conclusions. Obviously, this paper is not proving / supporting any theory, since it does not contain any survey or other modeling method. But on the other hand it also does not contain any hint for the method used for theory creation.
Christopher, M., & Lee, H. (2004). Mitigating supply chain risk through improved confidence International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 34 (5), 388-396 DOI: 10.1108/09600030410545436







Add new comment