Process oriented Approach to Supply Chain Risk Management
Supply Chain Risk Management started from the need to better control the risks within Supply and Demand Networks. The processes in (Corporate) Risk Management have been developed and convene in the classic, cyclic processes:
- Risk Identification
- Risk Assessment
- Measures (Development and Implementation)
- Risk Monitoring
Risk Management Process in the Network Environment
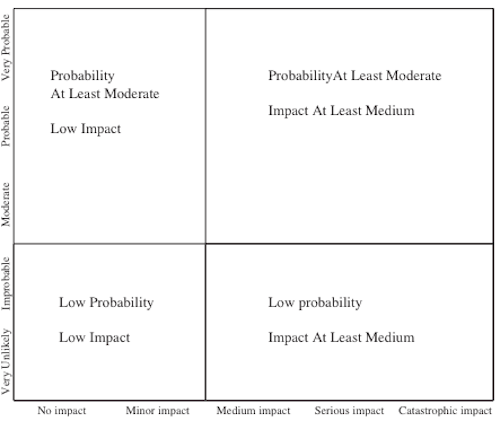
The authors start with a description of the general steps in the risk management process. The risk assessment is done using a semi quantitative diagram (Figure 1). For the risk management phase the authors suggest the following strategies:
- Risk transfer
- Risk taking
- Risk elimination
- Risk reduction
- Further analysis of individual risk taking
So up to now this information can also be found on wikipedia, but the genuine part starts with the “network risk management process”, where additional focus has to be put on how to integrate new aspects of collaboration and cooperation. The key is to add a seperate process of mutual risk identification, assessment, … and to feed insights from the individual risk processes into the mutual risk monitoring process. Figure 2 exhibits the details.
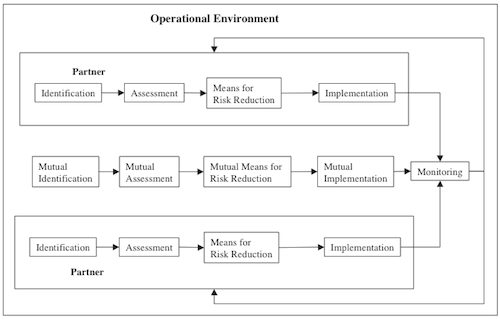
Deeper Understanding of Network Risks
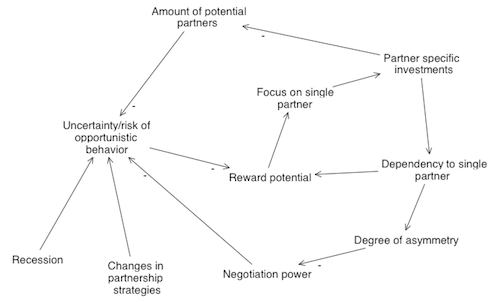
Nevertheless it is important to stress the importance of in depth analysis of the network risks. It is likely that simplistic methods for risk identification sometimes used in a corporate environment are not sufficient for a network setting. Increased complexity and additional risks increase the chance of missing important risks. As an example for a more suited method the authors cite a case study using systems dynamics analysis (see figure 3).
Conclusion
Goal of the mutual risk assessment process is to benefit both partners, the paper describes some challenges of risk management in a cooperative environment. Communication between the companies on their views on risks can therefore help to find adequate strategies to deal with the risks.
Hallikas, J., Karvonen, I., Pulkkinen, U., Virolainen, V., & Tuominen, M. (2004). Risk management processes in supplier networks International Journal of Production Economics, 90 (1), 47-58 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2004.02.007







Add new comment